
As the volume of data being generated around the world continues to grow, so does the need for faster, more efficient processing. Traditional cloud computing has served us well for over a decade, but it's beginning to show limitations—especially when speed, latency, and bandwidth are critical.
Enter Edge Computing—a revolutionary approach to data processing that brings computation closer to the source of data generation. Instead of sending all information to centralized data centers or the cloud, edge computing processes it locally—right where it's created.
This shift is not just a trend—it’s a fundamental evolution in computing. Let’s explore what edge computing is, how it works, and why it’s essential for the future.
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that moves data processing and storage closer to the devices and sensors that produce data—such as IoT devices, smartphones, or industrial machines.
In contrast to cloud computing, which sends all data to remote data centers for processing, edge computing performs analytics and decision-making at or near the data source, drastically reducing latency and dependence on internet connectivity.
In short: Edge = Process data locally
Cloud = Process data remotely

Cloud computing is powerful, but it has limitations in scenarios that require:
In such cases, routing everything to and from the cloud creates delays, increases bandwidth costs, and can expose systems to downtime risks.
Edge computing addresses these challenges by bringing intelligence and processing closer to the edge of the network.
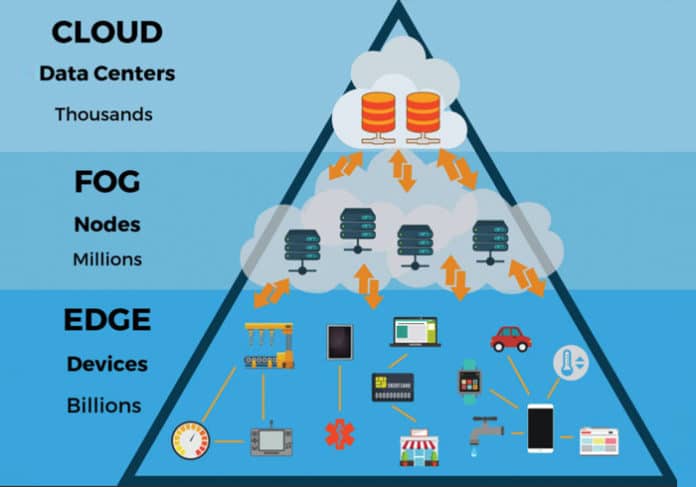
Edge computing typically involves:
The system decides what to process locally and what to send to the cloud, creating a balanced architecture that optimizes performance and cost.
Lower Latency
Processing happens near the source, enabling faster responses—crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles or remote surgery.
Reduced Bandwidth Costs
Only necessary data is sent to the cloud, reducing the load on networks and lowering infrastructure costs.
Improved Reliability
Systems can function independently of cloud connections, ensuring uptime even in remote or offline conditions.
Enhanced Privacy and Security
Sensitive data can be analyzed locally before being encrypted and sent to the cloud—or never sent at all—minimizing exposure.
Scalability
Edge devices can be deployed across diverse geographic locations, supporting scalable, localized computing without expanding centralized infrastructure.
Smart Cities
Edge computing powers intelligent traffic management systems, public surveillance, environmental monitoring, and emergency response systems with real-time data.
Healthcare
In hospitals or remote medical settings, edge devices enable real-time diagnostics, monitoring, and even predictive analytics without cloud delays.
Manufacturing & Industry (IIoT)
Smart factories use edge computing to monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and automate production lines with minimal latency.
Retail
In-store edge devices analyze customer behavior, manage inventory, and enable personalized experiences without cloud dependency.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on edge computing to process data from sensors, cameras, and lidar systems instantly to make split-second driving decisions.
Remote Work and VR/AR
With edge computing, immersive technologies like augmented reality and virtual collaboration platforms become smoother and more responsive.
While edge computing offers many advantages, it also comes with its own set of challenges:
Despite these concerns, the long-term gains in speed, efficiency, and cost make edge computing a strategic move for future-focused organizations.
Edge computing is not replacing the cloud—it’s complementing it. The future is hybrid: using both edge and cloud computing where each makes the most sense.

In the coming years, we’ll see:
Edge computing is not just about faster processing—it’s about reshaping the way we design and deliver digital experiences.
Edge computing is a transformative technology that brings data processing closer to where it matters most—at the source. For businesses that require real-time responsiveness, high efficiency, and localized intelligence, edge computing offers a powerful alternative to relying solely on cloud infrastructure.
As more devices become connected and the demand for low-latency solutions grows, edge computing will play a central role in the next phase of digital innovation.
Whether you're exploring edge-enabled IoT solutions, real-time analytics, or hybrid architecture, our team can guide your transition to an edge-powered future.
Contact us today to discover how edge computing can elevate your business performance.